Cloud Logging Overview
Cloud Logging Overview
20 August 2021
Cloud Logging stores logs across all GCP products and provides us with the facilities like searching, monitoring and alerting capabilities.
It comes with an API to ingest customized log data from any data source. It’s fully managed service, so there are no hard drives to provision or to divisions to resize. It ingest application and system log data from thousands of sources simultaneously.
Logs are made up of entries created by google cloud services, third party applications or by your own code.
Message carried by the log entries are called the payload and it can be unstructured data or strings
Examples:
Details of a compute engine instance starting up, a new file being uploaded to a bucket, calling to a Machine learning API, or Anything your application writes to the standard or error outputs.
Each log entry indicated where it came from by including the name of the monitored resources.
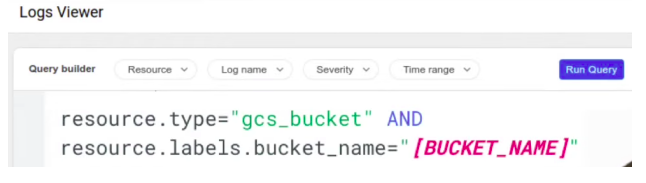
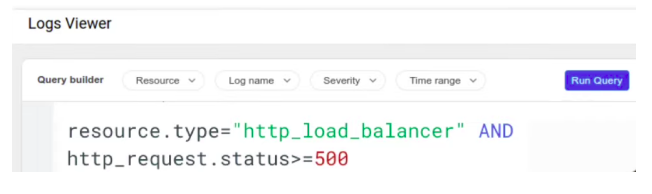
Using the console’s log viewer, we can query logging data and can obtain the clear subset of logged entries of the project.
The query will let us to find entries for a given resource from different namespaces based on the log level and of course by timestamp
Viewing and searching logs
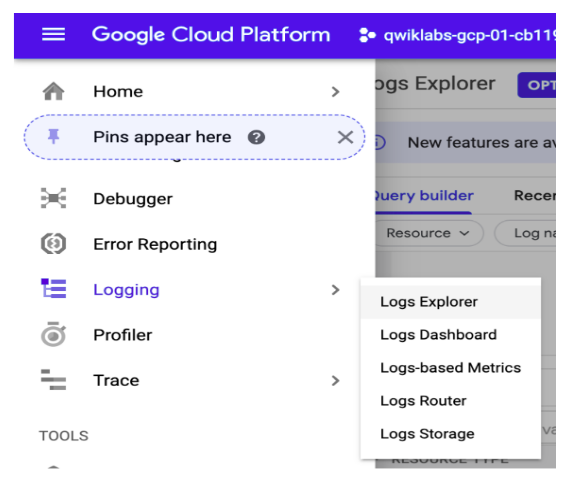
Navigate to Cloud Logs Explorer to configure which logs you view. Go to the Navigation menu > Logging > Logs Explorer.
Audit logging
Google Cloud provides Auditing of all Google Cloud resources by default. The audit logs give us the answer to the question “Who did what, when”, We can start by creating a new Compute Engine (Compute Engine) virtual machine (VM). To Launch a VM is an example of an audited activity, that it generates logs.
Audit log events
- In the Cloud Console, select Navigation menu > Compute Engine > VM instances.
 Wait for the Compute Engine service to initialize.
Wait for the Compute Engine service to initialize. - Click Create Instance
- Set the following field to the values below, leave all others at default.
- Click Create
Exporting logs
Cloud Logging retains logs for 30 days, after which they are deleted. To retain logs longer, you should export them to another storage system, or “sink”, such as BigQuery. Cloud Logging allows you to set up automated exporting jobs so that all logs will automatically be exported. Logs may then be further analyzed with the features of your chosen sink.
Kinds of logs
Google Cloud platform logs:
Google Cloud platform logs are basically service based logs that can help you debug and troubleshoot issues, as well as better understand the Google Cloud services you’re using.
The Google Cloud platform logs are visible to us in Cloud Logging, depending on which Google Cloud monitored resources that we are using in the Cloud project, folder, organization.
User-written logs:
User-written logs are mainly written to Cloud Logging by the user in one of the common ways that users write by their own logs.
Agent logs:
The Logging agent is a process that collects logs from user applications and writes them to the Cloud Logging API.
Security logs:
Cloud Logging provides two types of security-related logs, Cloud Audit Logs and Access Transparency logs.