Edge Computing: The future of computing and next-generation connectivity
Edge Computing: The future of computing and next-generation connectivity
08 April 2021
You must have heard about cloud computing earlier. In cloud computing we deal with the activities like data management, data storing and data retrieving from any other device just by using a virtual network or internet. Today, we will know something about edge computing and how it will be useful in next generation technology.
History?
In the 1990s, The main concept of edge computing was taken when Akamai solved the challenge of Web traffic congestion by introducing Content Delivery Network (CDN) solutions. The technology included network nodes that cached static media in locations closer to the end users.
Today, edge computing takes this concept further, introducing computational capabilities into nodes at the network edge to process information and deliver services to the end user.
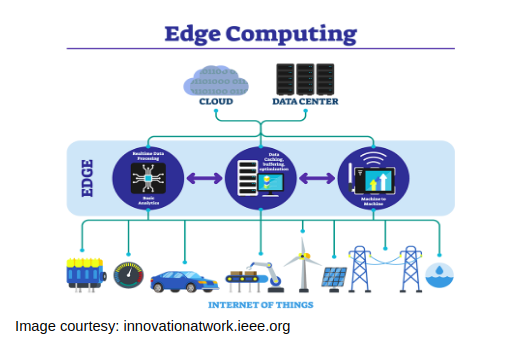
What is Edge computing?
Edge computing is an enhanced version of cloud computing. Both are the non-interchangeable technologies that cannot replace one another. In edge computing, data is processed or analyzed by the device itself or by a local computer or server rather than being sent to the data center or main cloud. Edge computing means running the processes at the edge of the client, such as in the user’s computer, or in an IoT device, or in any edge server that is connected with the internet and near to the client’s location. Here we are bringing the computation to the network’s edge that minimizes the long-distance communication between a client and server. It also reduces the latency, bandwidth usage and strain on main computing servers that accelerate real-time data processing. The important takeaway is that the edge of the network is geographically close to the user’s device unlike origin servers or cloud servers.
In edge computing, you need an external device or resource. Usually, in cloud computing, we see 2 servers in function, cloud server and user’s device. However in edge computing, we have 3 servers – one extra node in between the end user’s device and a cloud server that will be called an edge device.
Applications?
Autonomous vehicle: As the edge computing technology can provide us with real-time data without any delay, so it will be really useful in self-driving cars where the sensors or IOT devices of the vehicles require real-time data of the traffic around. By using that, autonomous vehicles can communicate and can run easily without any collisions. It will be helpful in effective city traffic management.
In Agriculture: Temperature and humidity sensors in agriculture fields collect valuable data, but that data isn’t analyzed or sorted in real time. Edge devices can collect, sort, perform preliminary analysis of that data, and then send it to centralized applications or some form of long-term storage, either in the cloud or on-premises. This traffic will not be time sensitive or slower, and because the data is presorted at edge network so the volume of traffic that needs to be sent will reduce. The upside of the edge computing is the faster response time for application that requires. The downside can be security concern as data will sort and analyze at edge so, it important to assure the security of the IoT device.
There can be many other applications possible with edge computing like, patient monitoring in hospitals, traffic management, remote monitoring in oil and gas industry, predictive maintenance, etc.
Challenges?
The current infrastructure of the network is not competent enough to support the real-time data processing with IoT or edge devices. We need the stronger network with high frequency waves and more small base stations to run the process smoothly. We need a full setup of network providing devices and it is something where we enter in the next generation model that is 5G. The implementation of the true 5G network is a challenge itself.
The other challenge is the security of the edge devices. To secure the personal data or real-time data in edge devices, we have to come with an advanced cyber security system that could be fit for edge devices.
Although, the need of an on-demand compute, real-time data processing and Internet of things will increase the uses of this technology and this human brain will definitely find a way to overcome these challenges.