Virtual data center overview:
Virtual data centers are a pool of cloud infrastructure resources specifically designed for enterprise business needs – a virtual representation of a physical data center, complete with servers, storage clusters and lots of networking components, all of which reside in virtual space being hosted by one or more actual data centers. Multiple virtual Unix/Linux or Windows servers can be run on a single machine. These virtual machines are created and managed through a software suite such as VMware.
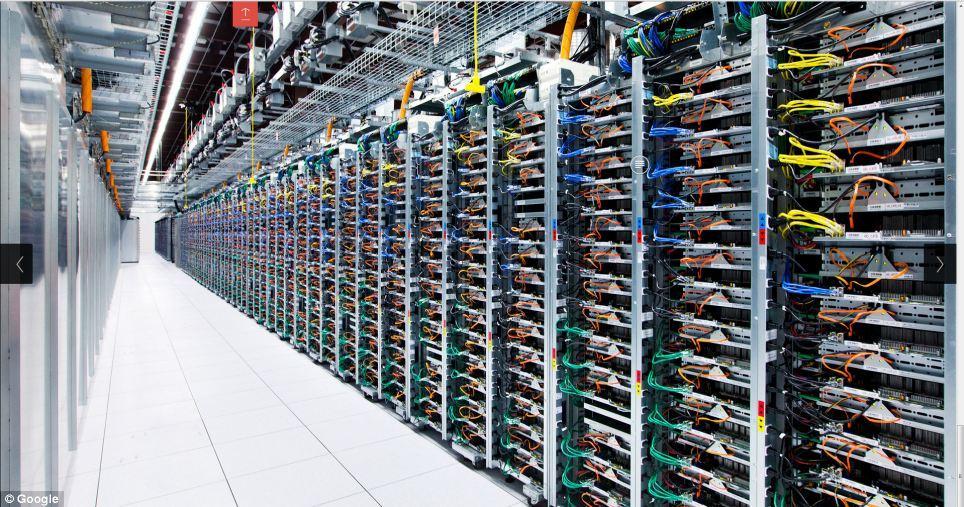

The Data Center offers cost predictability, hardware certainty, and control. However running and maintaining traditional data centers requires a lot of administrative overheads such as physical infrastructure, network structure, physical security, and capacity.
Additional benefits of the Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
The Google Cloud Platform (GCP) overcomes human efforts & provides additional benefits given below:
-
High-performance virtual machines:
GCP provides fast and consistent access to the memory you need, high IOPS, low latency and avoid noisy problems.
-
Auto-scaling:
GCP provides auto-scaling that helps your application grow and shrink its capacity even when you experience a spike due to extremely high traffic.
-
Security:
Google Data Center can offer high levels of security, using various layers of security such as security lasers, biometric detectors, alarms, cameras, and all of that cloak-and-dagger stuff.
-
Multi-regional redundancy:
Multiple data-center regions and zones across the world ensure the redundancy and availability of data in case of data failure.
-
Capacity and bandwidth:
GCP resolves the utilization and scalability issues as you can scale up and scale down your VM instances as per your requirements.
-
Facilities and support:
GCP takes care of installing or maintaining physical data-center hardware and allows you to focus only on running your application.
-
Network infrastructure:
GCP allows you to configure your network entirely through Cloud Platform’s service APIs and user interfaces. You don’t have to manage data-center networking hardware.
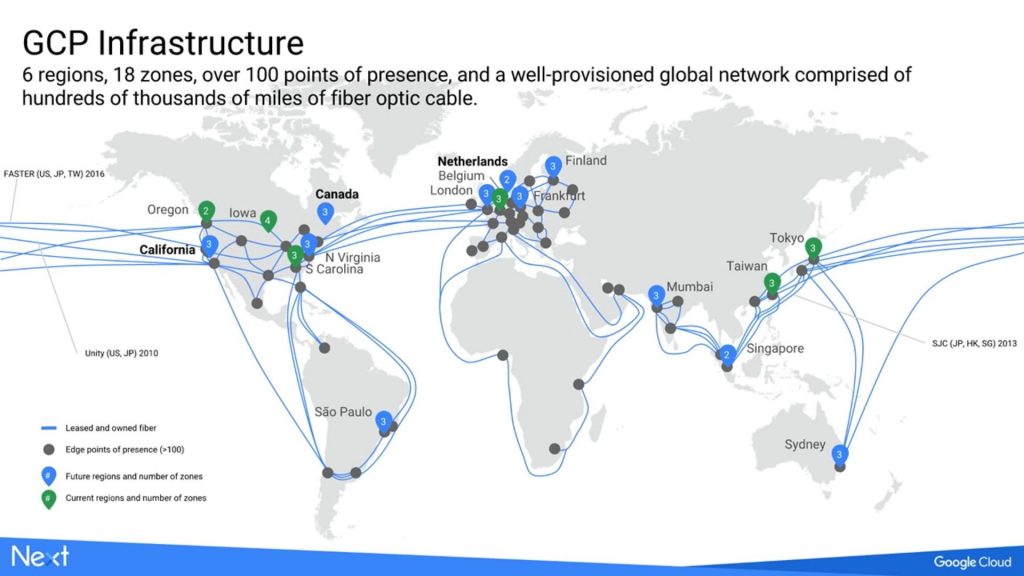
Google’s Cloud data centers location:
-
Council Bluffs, Iowa, USA
-
St. Ghislain, Belgium
-
Changhua County, Taiwan
-
Sydney, Australia
-
The Dalles, Oregon, USA
-
Ashburn, Virginia, USA
-
Moncks Corner, South Carolina, USA
-
São Paulo, Brazil
-
London, UK
-
Frankfurt, Germany
-
Jurong West, Singapore
-
Tokyo, Japan
-
Mumbai, India
-
Montréal, Canada
-
Netherlands
-
Hamina, Finland
-
Los Angeles, California
The Cost to Build Google Cloud Data Centers:
Google invested $1.2 billion to build the data center at The Dalles in Oregon, a 164,000-square foot building in 2016, while the newest data center in Eemshaven, Netherlands cost $773 million.
Water Pipes in Google Cloud Data Centers:

Air conditioning is great for humans but not for processors. It is not sufficient for cooling down a server. So, Google developed a system to cool down its servers with recirculating water. In the above image, those blue pipes, that’s cold water running to the servers while in Red pipes, hot water returning from the server.
Cold water runs from the cooling plant to the data center floor, where it is used to extract heat from inside the ‘hot huts’. The warm water is then returned to the cooling plant where the waste heat is removed, and the water is cycled back to the data center floor.
I want to conclude my topic as Data Centers under Google is highly secured, quickly accessible, scalable as per the requirements, and always available in various regions across the world. The Data Centers in Google are eco-friendly and not harmful for the environment as they are using Water Pipes to cool down its servers with recirculating water. So, Google is really taking our present to the future.
Also, you can read about the Introduction of Kubernetes on Google Cloud.