02 April 2021
What is a Microservice?
- A Microservice is a unit component of a system. It is built by connecting the components that can communicate using the APIs.
- While designing an application using the Microservice architecture, the application is structured as a collection of services
Features of a Microservice
- A Microservice is self independent. It can be deployed independently
- A Microservice can interact with any number of services or different type of Clients
- A Microservice can consist of various technologies and programming languages
Creating a Microservice
Open the Visual Studio in your machine and create a new project.
Select the application as ASP.NET Core Web Application and name it properly
Select API as the type of the project and “Enable Docker Support” with OS type as Linux.
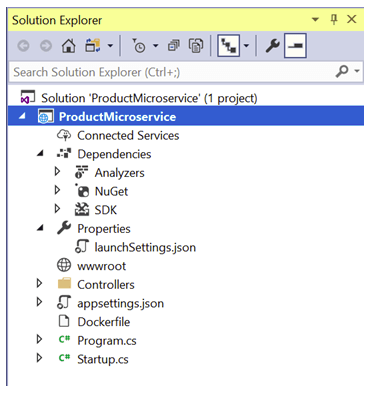
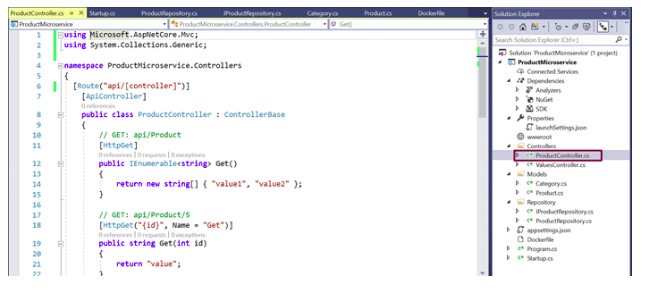
The solution will look like as
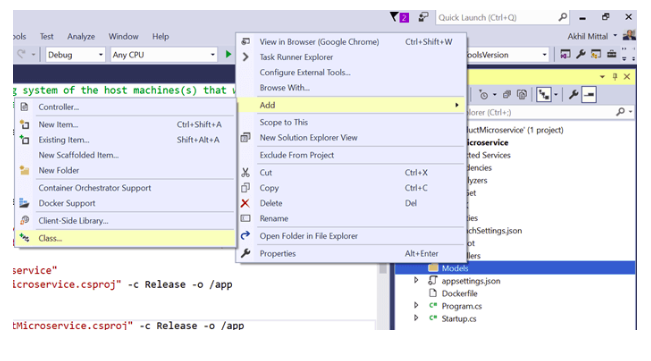
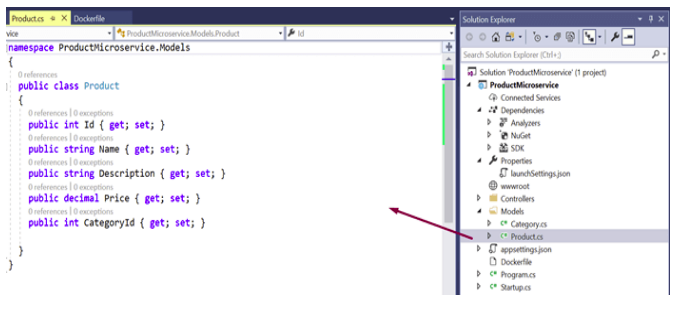
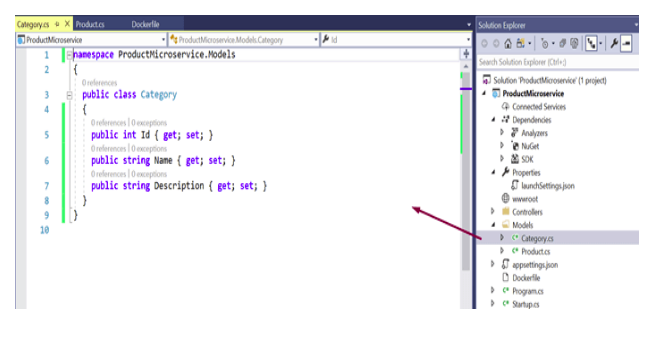
Add Models classes to that Project
Add some fields like Id, Name, Description, Price to the model classes. Add the proper fields as per your requirement.
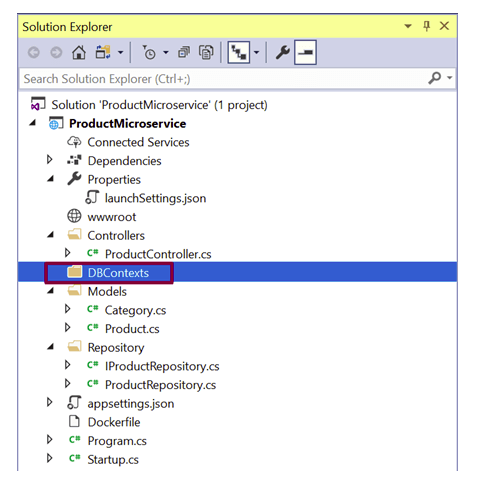
Enable Entity Framework Core and add EF Core DbContext. A database context is needed so that the models could interact with the database. Create a folder named DbContexts to the project.
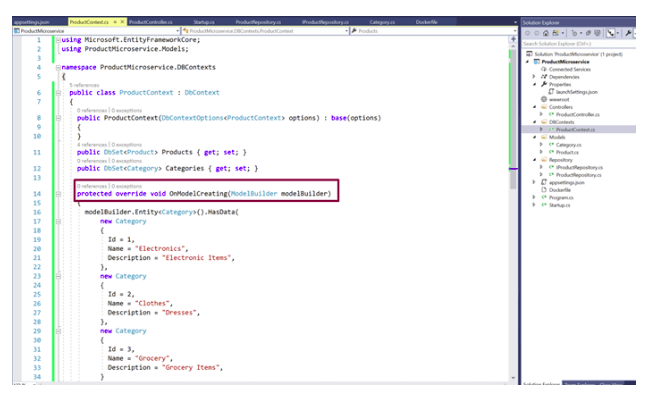
Create a class named ProductContext which contains the DbSet properties for Products and Categories. OnModelCreating is a method through which the master data could be inserted to the DB. Hence, create the OnModelCreating method and add some sample categories that will be added to the DB initially into the table when the DB is created.
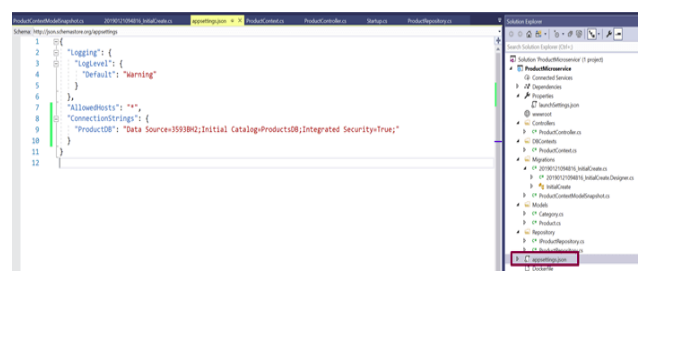
Add the connection string
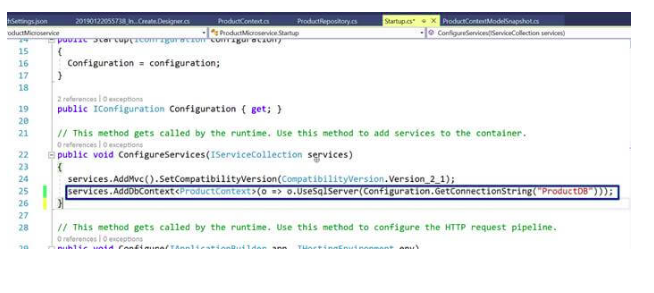
Modify the Startup.cs file and add the SQL server db provider for EF Core.
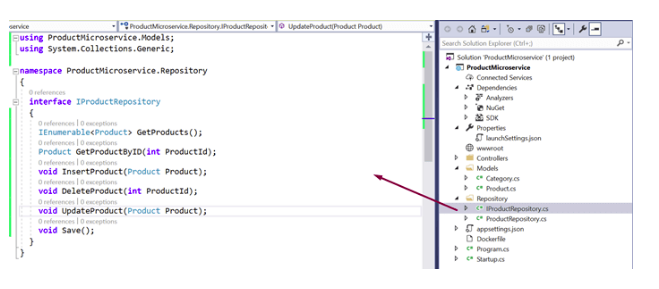
Create Repositories and their interfaces. Add the methods in the interface that performs CRUD operations for Product microservice.
Create a new class named ProductRepository in that same Repositories folder that implements interface IProductRepository. And add the implementation for the methods by accessing the context methods. Modify the Startup class and add the code as services.AddTransient<IProductRepository, ProductRepository>(); in the ConfigureServices method
Add Controllers to the Project by selecting ‘API Controller with read/write actions ’
Implement the methods by calling the repository methods as shown in the below code.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using ProductMicroservice.Models;
using ProductMicroservice.Repository;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Transactions;
namespace ProductMicroservice.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class ProductController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IProductRepository _productRepository;
public ProductController(IProductRepository productRepository)
{
_productRepository = productRepository;
}
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult Get()
{
var products = _productRepository.GetProducts();
return new OkObjectResult(products);
}
[HttpGet("{id}", Name = "Get")]
public IActionResult Get(int id)
{
var product = _productRepository.GetProductByID(id);
return new OkObjectResult(product);
}
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Post([FromBody] Product product)
{
using (var scope = new TransactionScope())
{
_productRepository.InsertProduct(product);
scope.Complete();
return CreatedAtAction(nameof(Get), new { id = product.Id }, product);
}
}
[HttpPut]
public IActionResult Put([FromBody] Product product)
{
if (product != null)
{
using (var scope = new TransactionScope())
{
_productRepository.UpdateProduct(product);
scope.Complete();
return new OkResult();
}
}
return new NoContentResult();
}
[HttpDelete("{id}")]
public IActionResult Delete(int id)
{
_productRepository.DeleteProduct(id);
return new OkResult();
}
}
}
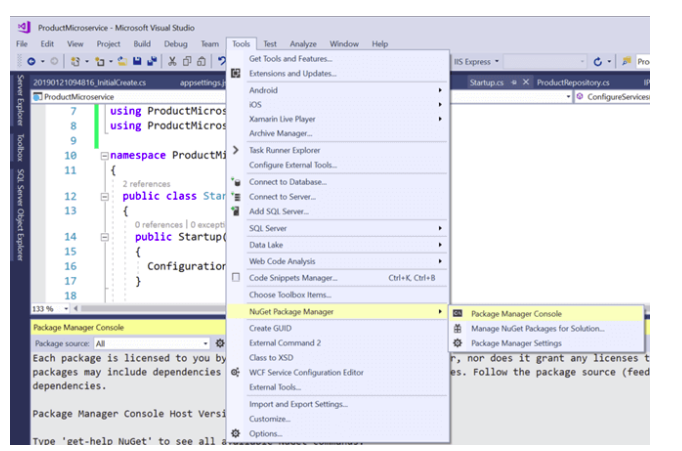
Perform EF Core Migrations and open Package Manager Console
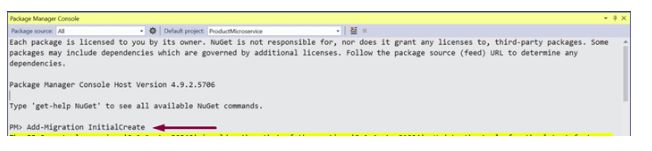
For enabling the migration, type the command, Add-Migration and give that a meaningful name for e.g. InitialCreate and press enter.
Execute ‘Update Database’ command to ensure that the migrations are applied to the database
Open the SQL Server Management Studio to check if the database got created or not.
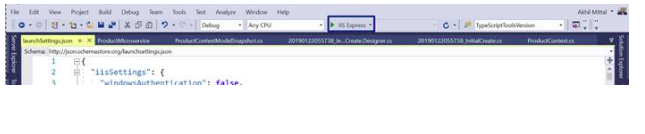
Run the Product Microservice using the IIS Express as shown below
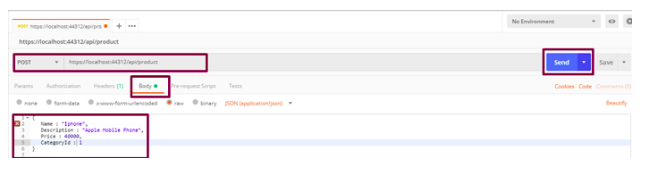
Use Postman to test the POST method by providing the endpoint and a JSON having properties of Product model in the Body section. Response will be returned with the product ID.
Check the DB and execute a select query on the table created in the DB, a new added row will be shown for the newly created product.