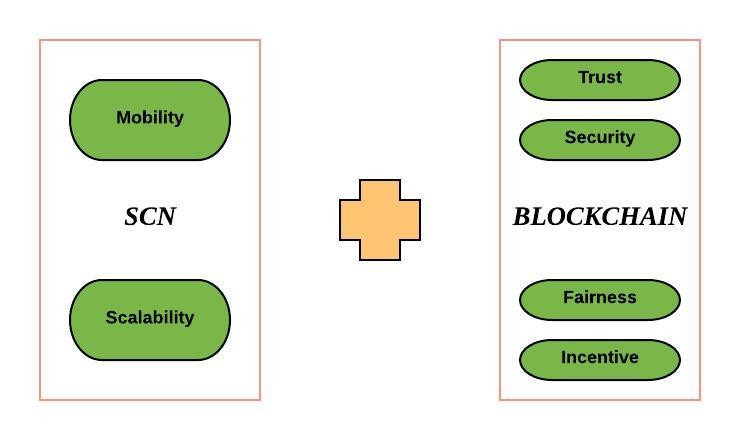
In today’s world, we are connecting billions of devices with a large influence in people’s lives. Many think that the future of IoT is being threatened by the delicate connectivity, poor extensibility, confidence deficit, splintered security and scattered business model. Using BlockCloud technology, the practitioners have provided a method named Service-Centric Networking (SCN) which gives us reliable connectivity and global scalability, however, security and incentive of services becomes difficult to guarantee. The different direction to use blockchain technology to achieve a trust, secure and incentive IoT. BlockCloud is a new step that combines the advantages of SCN and blockchain to empower IoT. It is a service-centric blockchain architecture, which leverages a service-driven communication prototype to support mobility and scalability.
It is a ‘Universal Overlay’: it can run over anything including IP. Thus, BlockCloud shows us different trump cards such as service distribution, application-friendly communication, naming, robust security and mobility.
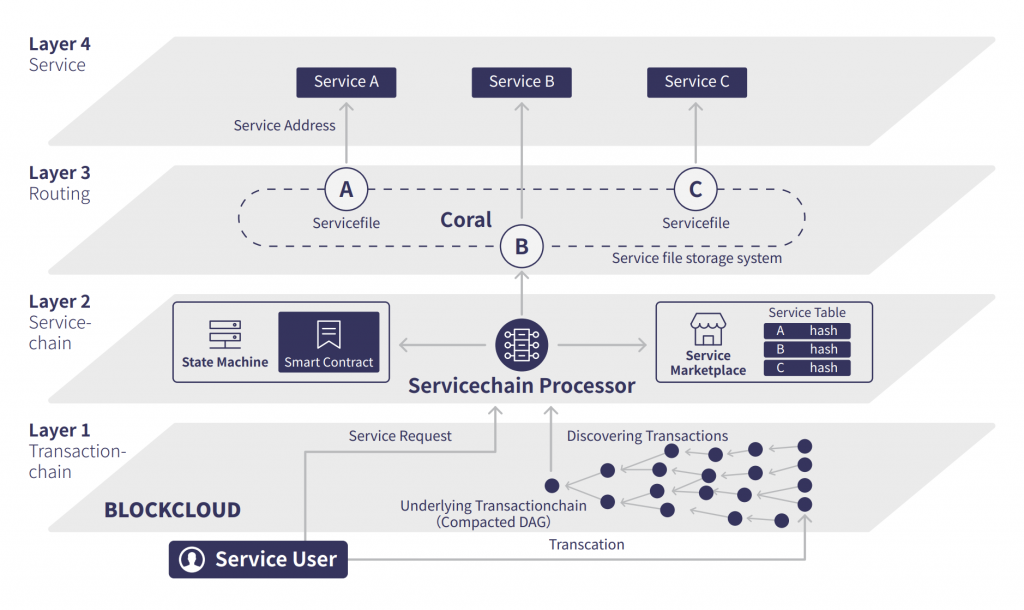
The BlockCloud Architecture:
-
Transaction-chain Layer:
The transaction-chain layer occupies the lowest tier as shown in the architecture. Operations regarding the blockchain are encoded on the underlying transaction chain. Currently, the Blockcloud team proposes to use Compacted Directed Acyclic Graph (CoDAG), which can be mathematically proved to be efficient for large-scale and dynamic IoT scenarios. CoDAG improves the traditional DAG structure to guarantee fast conformation time and liveness property.
-
Service-chain Layer:
It defines new operations without requiring changes to the underlying blockchain. Only BlockCloud nodes are aware of this layer. BlockCloud operations are defined in the service-chain layer and are always encoded in valid blockchain transactions as additional metadata. Blockchain nodes always see the raw transactions, but the logic to process BlockCloud operations only exists at service-chain level. To accept or reject any BlockCloud operations are defined by the service-chain layer. The accepted operations are processed by the service-chain to construct a database that stores information on the global state of the system along with state changes at any given blockchain block.
-
Routing Layer:
We see that blockCloud separates the task of routing requests from the actual providing of service. Now, this avoids the need for the system to adopt any particular management service from the onset and instead allows multiple service providers to coexist, including both commercial entities and peer-to-peer systems. The routing information, which is similar to DNS files, BlockCloud always uses this information as service files. Also, users don’t need to trust the routing layer because the integrity of service files can be verified by checking the hash (zone file) in the control plane.
-
Service layer:
It is the top-most layer which serves the actual services for the network. In this layer of service, the owner of the respective service signs all the service names accordingly. Here, BlockCloud allows arbitrary IoT services which are provided by a variety of IoT devices.
Advantages of BlockCloud:
-
Low-Latency:
It is a massive global edge network which connects to every geographical location at any time. Also, it takes a milli-second to respond against the service wherever needed. The service of this technology continues seamlessly without any hindrance during mobility.
-
Exceptionally Reliable:
It provides extra security and protection against malware functions. Reduce the chances of faulty steps performed by the service provider.
-
Easy Operation & Low Cost:
It always reduces the operations and maintains the costs greatly. We don’t have to allocate any resources beforehand and users will be charged only for what resources they have consumed.
-
High Extensibility
BlockCloud is an open-interfaces network; extensible to multiple programming languages and multiple development environments.
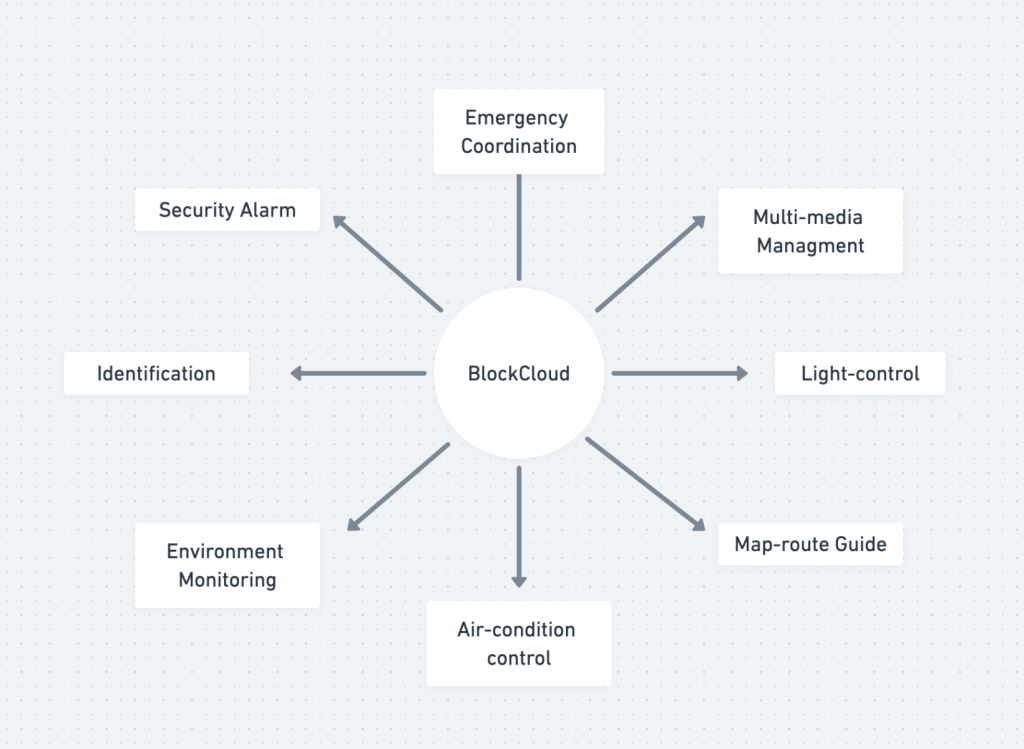
Use-Cases of BlockCloud: